In an era where data serves as a critical strategic resource, detecting anomalies in network traffic has become essential for preventing cyberattacks and ensuring data security. Such detection technologies also play vital roles in social media analysis, bioinformatics, financial regulation, and smart city transportation systems.
A research team led by Professor Xu Li from the College of Computer and Cyber Security at Fujian Normal University has recently made significant progress in detecting anomalies in high-dimensional complex data. Focusing on structural modeling and efficient learning of high-dimensional and high-order data, the team has developed integrated methods—including tensor low-rank recovery, centrality metrics, multimodal fusion, and meta-learning—to enable more interpretable and robust anomaly detection in real-world network environments.
In one key achievement, the team innovatively combined tensor feature representation with eigenvector-based edge centrality for network traffic anomaly detection. By constructing a tensor eigenvector “edge centrality” formulation to quantify link importance and incorporating centrality features with a Laplacian term into a model that integrates low-rank tensor recovery and representation learning, the method effectively captures nonlinear neighborhood and structural information. Not only does it improve the accuracy of random anomaly detection, but it also shows heightened sensitivity to targeted attacks originating from high-centrality links. Experimental results demonstrate marked advantages in precision, recall, and other key metrics. These findings have been published in the paper “Enhanced Network Traffic Anomaly Detection: Integration of Tensor Eigenvector Centrality with Low-Rank Recovery Models” in IEEE Transactions on Services Computing, a CCF Class-A journal in the field of service computing.
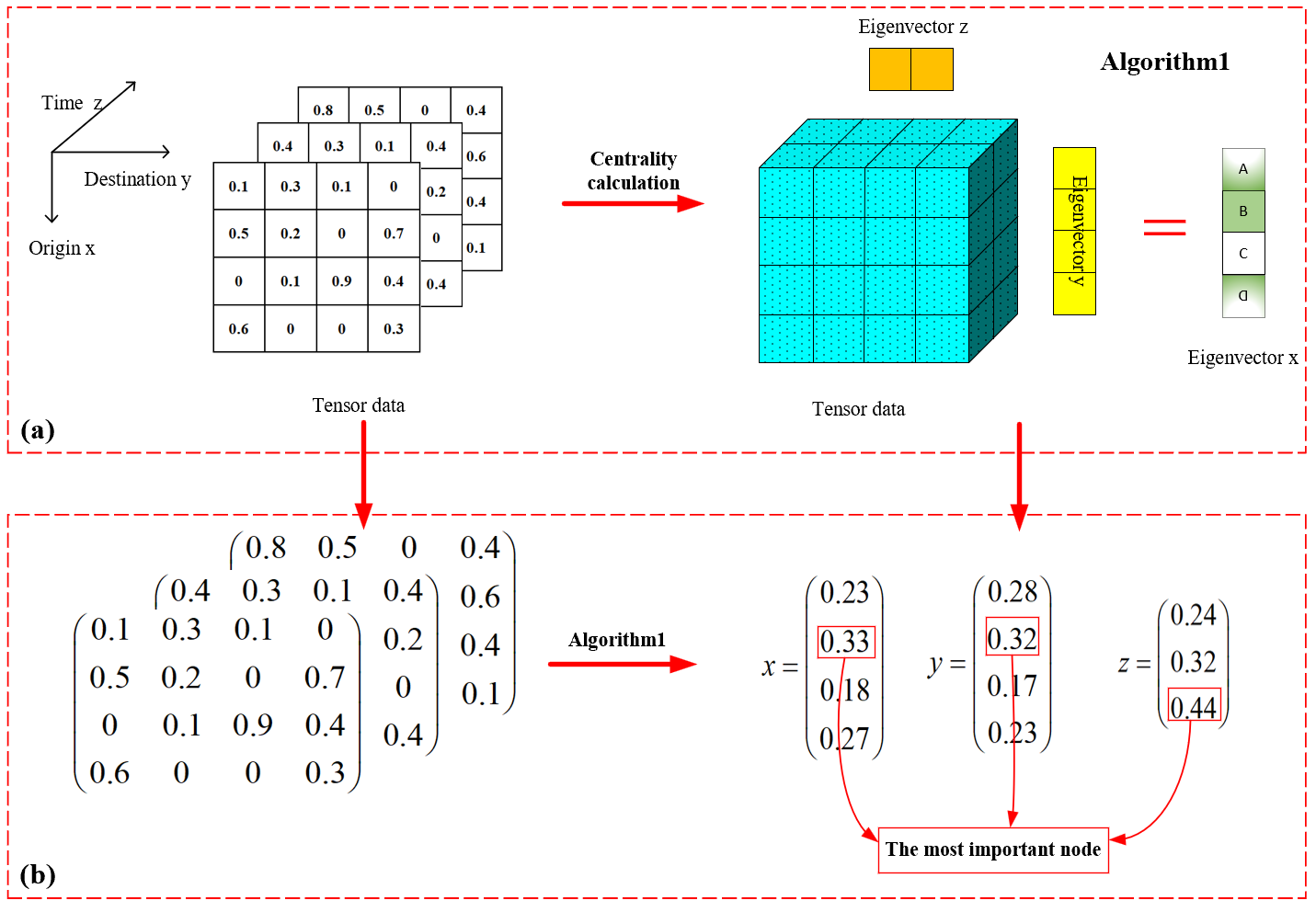
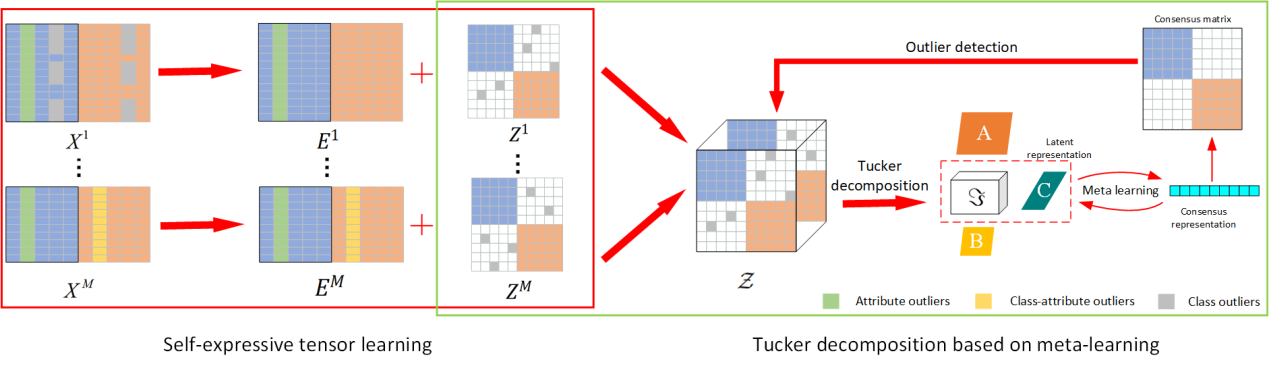
In another advancement, the team proposed a novel framework named LRTDM, based on low-rank Tucker decomposition and meta-learning. This approach uses Tucker decomposition to accurately characterize the low-rank structure of multi-view self-representation tensors. The resulting factor matrices and core tensor preserve latent structural features of each view while revealing shared information across views. By introducing meta-learning, the team modeled the learning and fusion of view-specific features as a bi-level optimization problem, solved through an alternating optimization strategy that enhances the recovery of consistent structures. During anomaly detection, the model leverages both the consensus matrix from latent representations and the error matrix from the self-expressive process, enabling more accurate identification of anomalies in multi-view settings. The related paper, “Low-Rank Tucker Decomposition for Multi-View Outlier Detection Based on Meta-Learning,” has been published in Information Fusion, a leading international journal in computer science and AI, recognized as a Tier-1 TOP journal by the Chinese Academy of Sciences with a 2025 impact factor of 14.8.
Both studies list FJNU as the first author affiliation and are the result of collaboration between Professor Xu Li’s team at FJNU and Professor Xie Kun’s team at Hunan University. Lin Wei, a Ph.D. candidate at FJNU’s College of Computer and Cyberspace Security, is the first author of the papers, with Professor Xu Li as the sole corresponding author. The research was supported by the National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars, the NSFC Regional Joint Fund, the NSFC General Program, the Central Government’s Special Fund for Guiding Local Science and Technology Development, and the Key Project of Science and Technology Innovation of Fujian Province.
